what is Viscosity?
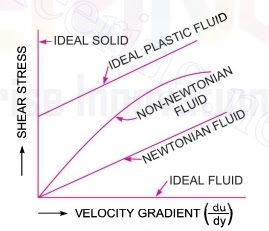
Viscosity is defined as the property of a fluid which offers resistance of the movement of one layer to of fluid over another adjacent layer of the fluid.When two layers of the fluid, a distance 'dy' apart, move one over the other at different velocities, say u and u + du , the Viscosity together with relative velocity causes a shear stress acting between the fluid layers. CLICK HERE
The top layer causes a shear stress on the adjacent lower layer while the lower layer causes a shear stress on the adjacent top layer.This shear stress is proportional to the rate of change of velocity with respect to y.It is denoted by symbol of 𝜏 (Tau).
Mathematically, 𝜏 ∝ du / dy
𝜏 = μ du / dy
where μ (mu) is called co-efficient of Dynamic Viscosity or only viscosity.
Again du / dy = dθ /dt i.e. rate of shear strain or velocity gradient.
The Viscosity is defined as the shear stress required to produce unit rate of shear strain. CLICK HERE
unit of Viscosity
The unit of Viscosity is obtained by putting the dimensions of the quantities in above equation.SI unit of Viscosity is N s/m^2 or Pa.s. Again it can be also expressed in MKS unit as Poise. CLICK HERE
1 N s/m^2 = 10 Poise
Kinematic Viscosity
It is defined as the ratio between the Dynamic Viscosity and Density of fluid.It is denoted by symbol ν (nu). CLICK HERE
Mathematically, ν = μ/ρ
unit of Kinematic Viscosity
By putting on above equation we get SI unit of Kinematic Viscosity is m^2/s.Again as Dynamic Viscosity it can be also expressed in MKS unit in Stokes.







No comments:
Post a Comment